
Nursing is a crucial component of the healthcare system. It aids in preserving the health and well-being of people of all ages. However, it has evolved significantly from the days of Florence Nightingale in the 19th century to the modern-day nursing profession, adapting to changing healthcare needs, technology advancements, and societal shifts.
Today’s highly skilled and specialized experts have revolutionized nursing from its early days when it was largely a volunteer-based profession. Nurses are now responsible for providing care, support, and comfort to patients in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities.
This article will explore the evolution of nursing throughout history. It highlights seven ways nursing has changed with time.
1. Rise of Online Learning
The emergence of online nursing education has been one of the most significant changes in the recent years. Many online nursing education programs use innovative and cutting-edge technologies like multimedia tools, virtual simulations, and online discussion forums to enhance the learning experience.
It allows nurses to finish their postgraduate degrees and certifications while still working and juggling personal commitments. These online programs are more affordable than classroom-based education with the same curriculum and courses as traditional on-site campuses.
For instance, an online MSN program offers coursework related to healthcare policy, advanced nursing practices, healthcare administration, and patient management. It provides an excellent opportunity for registered nurses to further their education, gain specialized skills, and advance their careers while maintaining their work and personal commitments.
2. Technological Advances
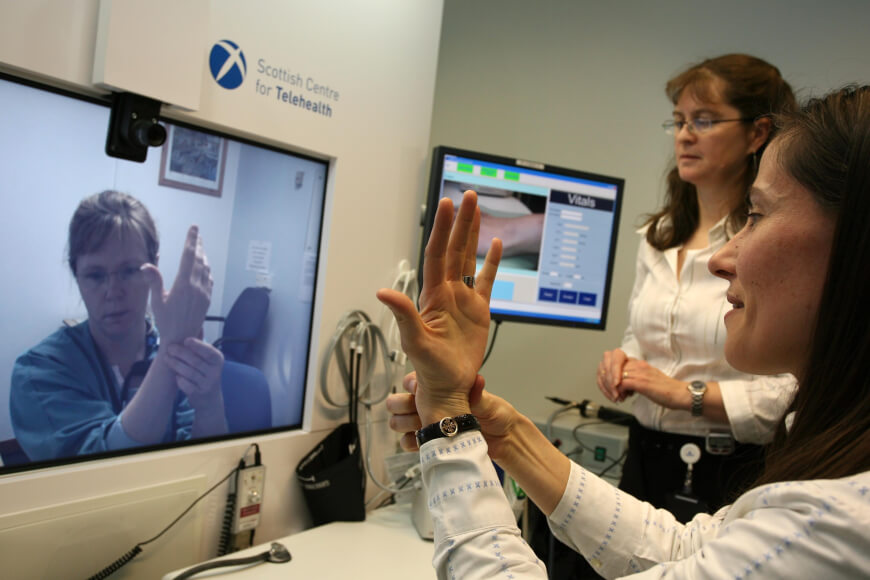
Early on, the responsibilities of nurses were limited to checking patients’ vital signs and interacting with other healthcare professionals. But with telemedicine, digitalized health data, and other technological advancements, nurses can now monitor patients from a distance, work remotely with their colleagues, and use artificial intelligence to diagnose patients more accurately.
Usage of mobile devices, patient portals, and wearable health monitors has become common. Thus, nurses have closer bonds with their patients. They can access patient records quickly, diagnose patients accurately, and create efficient treatment plans through electronic medical records (EMRs). While expanding access to healthcare, Telehealth enables patients to share their health information with their care providers in real time, making nurses offer more personalized care.
3. Patient-Centered Care
Patient-centered treatment depends on informed consent. It’s essential to prioritize patient choices, values, and wants when providing healthcare services. Previously, the disease or condition of the patients rather than the patients themselves was more of a focus for nurses and other healthcare professionals. Now, nurses collaborate with patients to help them reach their healthcare objectives because they see patients as active participants.
With access to digital information, people’s comprehension has increased to the point where they feel compelled to inquire further about their health. So, the nurses actively listen to their patients to understand their preferences and values and include them in decision-making.
They also assess patients’ physical and emotional needs to develop a personalized care plan.
4. Evidence-Based Practice (EBP)
The nursing practice used to be dependent on personal experience, but since the advent of EBP, nurses are now using scientific findings to guide their practice. EBP entails using data to inform clinical judgments and enhance patient outcomes. Reviewing research literature, critically evaluating the findings, and incorporating it into clinical practice are all part of its emphasis on employing research evidence.
Research repeatedly shows that EBP lowers costs, strengthens outcomes, reduces regional disparities in care, and improves healthcare delivery. EBP usage has been shown to lower burnout by raising overall job satisfaction. Due to the enhancements in patient outcomes and safety brought about by these advancements, it is now an essential part of nursing practice.
5. Specialization
A few decades ago, nursing was about providing primary care to patients, such as administering medication and assisting with daily living activities. But as healthcare has become more complex and specialized, nursing has followed suit. Specializations in nursing have allowed for more in-depth and specific patient care, leading to improved outcomes and better quality of care. Now, there are advanced practice nursing roles, such as nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, and nurse anesthetists.
These roles allow nurses to take on more advanced and specialized responsibilities, such as prescribing medication, diagnosing and treating illnesses, and performing medical procedures. It requires additional education and training in specialized areas of nursing, such as critical care, oncology, pediatrics, and mental health. Nurses with specialization in these areas have a deeper understanding of the unique needs and challenges faced by patients, allowing for more personalized and effective care.
6. Enhanced Regulatory Framework
Today, the practice of nursing is heavily regulated, with many rules, regulations, and standards of care. Regulatory organizations that guarantee nurses adhere to professional standards include the American Nurses Association and State Boards of Nursing. Through their rules and policies, they ensure that nurses treat patients safely, ethically, and competently.
To get licensed as a nurse, nurses must satisfy educational and training criteria and pass an exam. They must fulfill continuing education requirements to keep their licenses current and be informed about new developments and advancements in medicine. Moreover, the regulatory framework has improved nursing practice’s transparency and accountability. Nurses are now obligated to observe ethical and legal rules and keep accurate records of patient care.
7. Multiculturalism & Diversity
The patient population seeking medical attention is diversifying. As a result, more patients from diverse cultural and racial backgrounds come for medical help, making the nursing workforce more representative of the population it serves to keep up with this shifting demographics.
Nurses are now more likely to involve patients in their care and customize treatment plans to match each patient’s particular needs as they are more aware that patients have different needs and viewpoints based on their cultural and ethnic origins. Besides, nurses have now improved their communication abilities to guarantee that patients from varied backgrounds understand their health conditions, treatment options, and care plans. It helps them assist patients in making educated decisions regarding their health.
Conclusion
The evolution of nursing practice has been significant for both nurses and patients. It has developed into a highly specialized profession with many dimensions. Unlike before, nurses have now found themselves in an equal position with other healthcare professionals as they work side by side with major responsibilities. And with the current pace of advancement, it is only likely to take further steps in its pursuit of development.








